With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and increasing demand for real-time data processing, edge computing is reshaping and becoming a game-changer in the world of IT.
Edge computing has been gaining more and more attention in recent years as an innovative technology that can provide low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time processing capabilities to various applications.
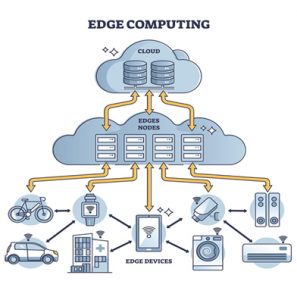
Simply put, "edge computing" refers to the practice of processing data at or near the source of its generation rather than sending it to a centralized data center for processing.
In this blog, we will explore what computing is, its benefits, and how it can transform the way we process and utilize data.
What is edge computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that makes it possible to process and analyze the data closer to the location where it was generated.
In traditional computing, devices collect data and send it to a central data center, where it is processed and analyzed. This approach is suitable for applications that do not require real-time processing or low latency.
Unfortunately, traditional computing doesn't work well for applications that generate a massive amount of data or need to be able to process it in real time, like self-driving cars, industrial automation, and smart homes.
But with edge computing, the processing and analysis of data occur at the "edge" of the network, near the source of data generation.
Edge computing as data network and storage technology
Putting edge devices like servers, gateways, or routers at the network's edge can accomplish this. These devices are often placed closer to the end-users than other devices or machines that generate data. They can process and store data locally, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central server or data center.
How does edge computing work?
Edge computing works by establishing a network of edge devices, which are small, low-power computing devices that are placed in proximity to data sources. These devices have sensors, processors, and storage, so they can collect, process, and analyze data in real time.
Once the data is processed, the edge devices can transmit it to a centralized data center for further analysis or storage. This approach cuts down on the amount of data that needs to be sent to the data center, which speeds up processing and decreases latency.
Benefits of edge computing
Edge computing offers several benefits over traditional computing, including:
Reduced latency
By processing data closer to the source of its generation, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel from the source to the data center and back. This is critical for real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
Enhanced security
Edge computing can make the network safer by reducing the amount of data that needs to be sent across it. With this, data is processed locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Improved reliability
Edge computing can improve reliability by reducing the dependence on a centralized data center. With edge computing, data can be processed and analyzed even if the network connection to the data center is lost.
Cost savings
Edge computing can result in cost savings by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the data center. This can lower bandwidth costs and reduce the need for expensive data center infrastructure.
Innovative applications of edge computing
Edge computing has lots of use cases across various industries, including:
Industrial automation
Edge computing is suitable for industrial automation, which needs to process data in real time to work well and keep people safe. Industrial automation systems can respond to changes in the environment in real time by processing data at the edge. This makes them more efficient and cuts down on downtime.
Autonomous vehicles
Autonomous vehicles require real-time processing of vast amounts of data to ensure safe and reliable operation. Edge computing can let this data be processed and analyzed in real time, which will cut down on latency and make things safer.
Find out more about smart transportation systems.
Healthcare
This can be used in healthcare to keep track of a patient's vital signs in real time. This lets doctors and nurses respond right away to changes in a patient's condition. Moreover, this can improve patient outcomes and reduce the need for hospitalization.
Explore also IoT healthcare solutions for the medical industry.
Retail
Edge computing can be used in retail to analyze customer behavior and preferences in real time. This lets retailers make personalized recommendations and improve customer shopping experiences.
Discover more about Robustel’s smart retail solution
Edge computing represents a significant shift in the way we process and utilize data.
By processing data at the edge, we can cut down on latency, improve security, make the system more reliable, and save money. With its many use cases across various industries, edge computing is poised to become a major force in the world of IT.
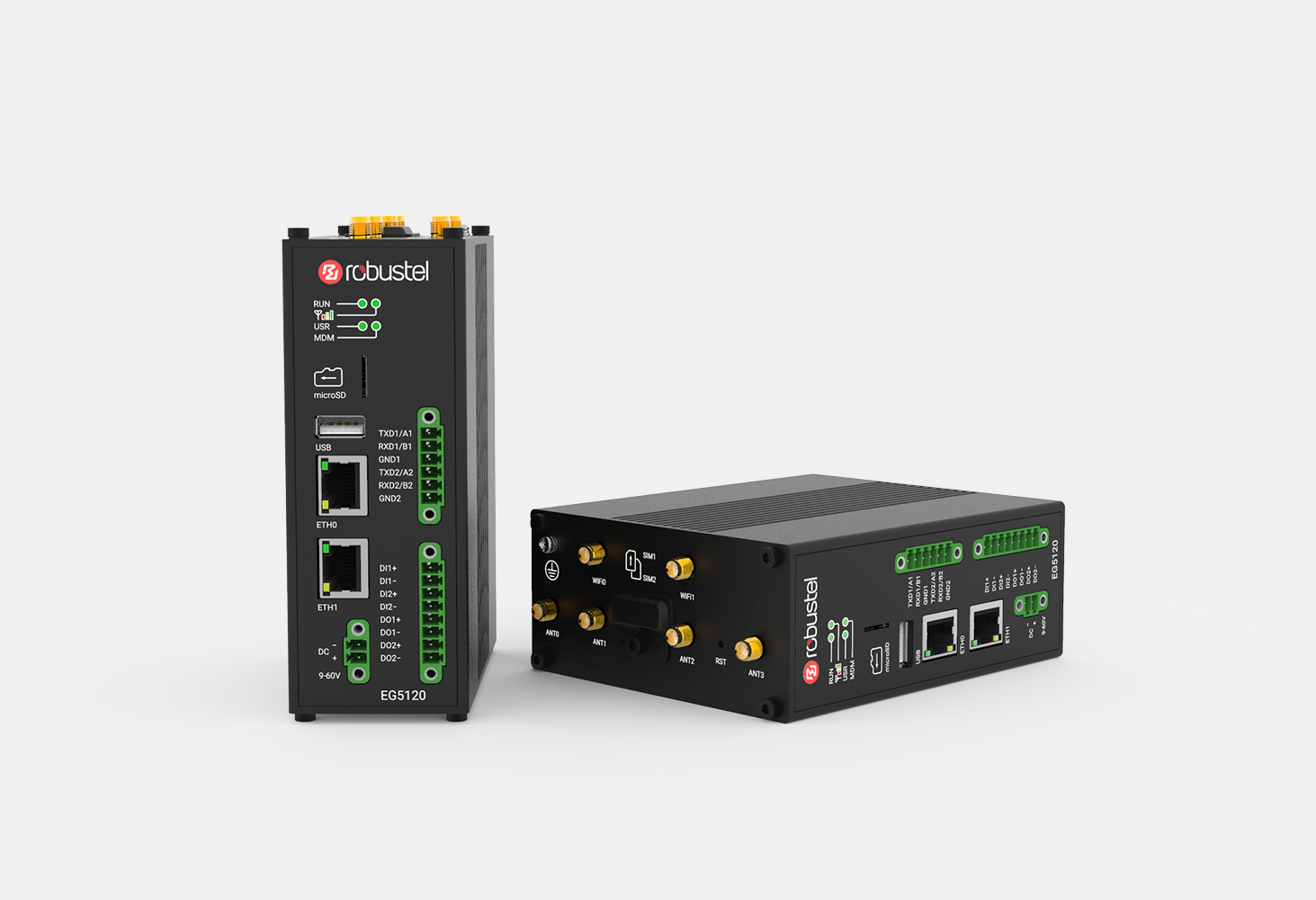
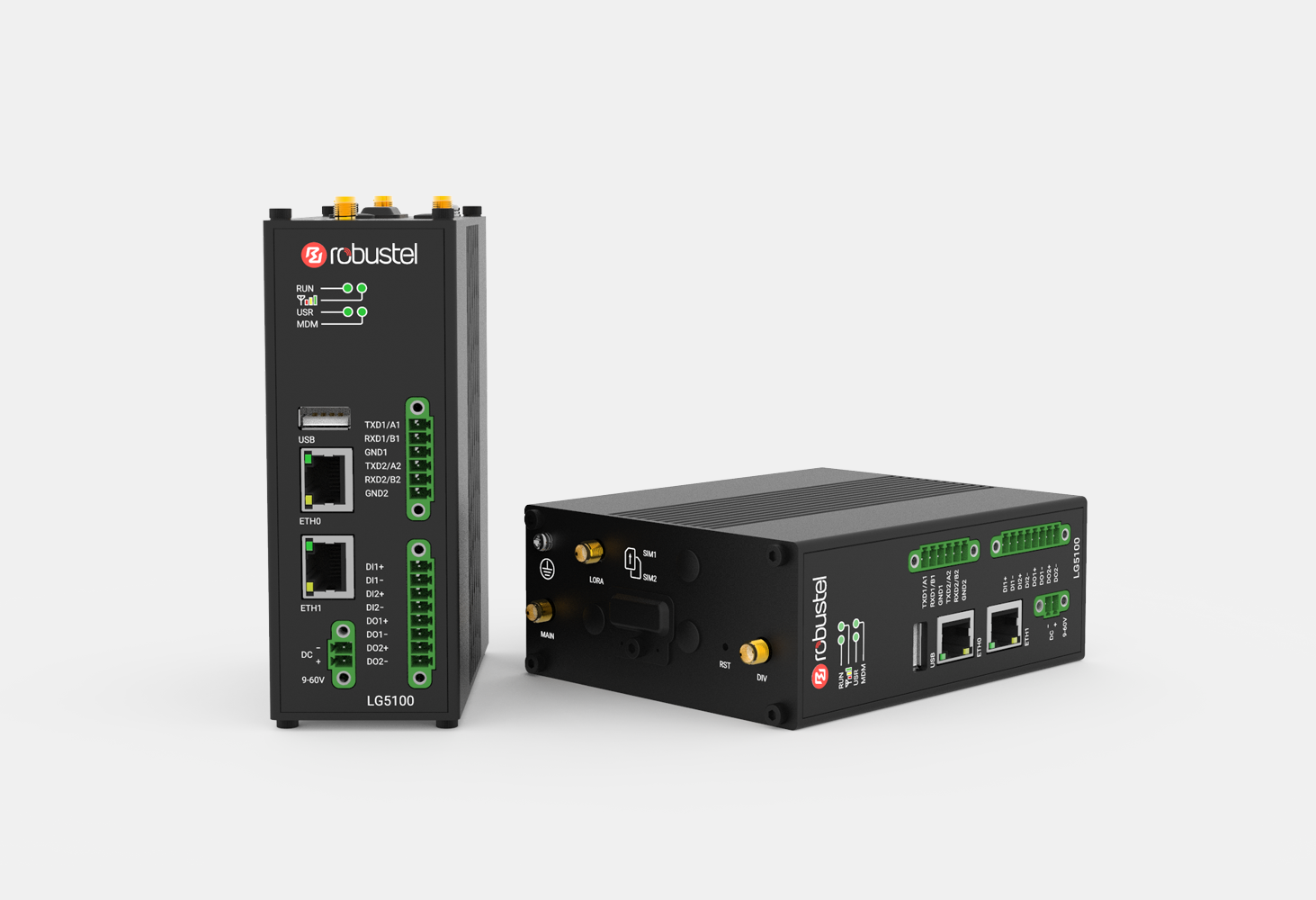
Connect your industrial edge computing gateway with Robustel!
The industrial edge computing gateway from Robustel is truly a powerful way to connect edge computing and intelligent decision-making.
With its advanced technology, the gateway connects to and manages data from multiple sources. This gives real-time insights that can be used to improve industrial processes, save money, and make them more efficient. It is made to work well in harsh industrial environments, which makes it a reliable and long-lasting tool for managing and analyzing data.