NB-IoT and LTE-M are two versions of Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies. They offer low power consumption and wide coverage, making them ideal for connecting low bandwidth, long-range devices. NB-IoT was standardized by 3GPP in Release 13, while LTE-M was standardized by 3GPP in Release 14.
Network coverage is an important factor to consider when deploying Internet of Things (IoT) applications. These types of connections require good network coverage to ensure a robust connection for the various IoT applications.
Unlike human beings, IoT installations such as smart meters are unable to change position in order to obtain a better signal, due to the fact that they are often installed in places such as basements or other areas with limited reception. Therefore, it is important to ensure that there is good network coverage when deploying IoT applications, so that the connection can remain reliable and consistent.
Therefore it is essential to know how to take accurate and reliable measurements of NB-IoT and LTE-M network quality. Here are some tips and tricks to help improve your network quality measurements with your Robustel routers:
Run Tests During Different Times of Day
Run measurements during different times of day in order to assess how the network responds at peak and low usage times. This will provide a better understanding of how the network performance varies throughout the day.
Utilize RobustOS Dashboard Features
RobustOS is Robustel's proprietary router operating system which houses tools such as web GUI, script execution, API interface and dashboard features that will all help you get accurate and reliable measurements. The network quality value can be found at WEB GUI of RobustOS — Interface — Cellular — Status.
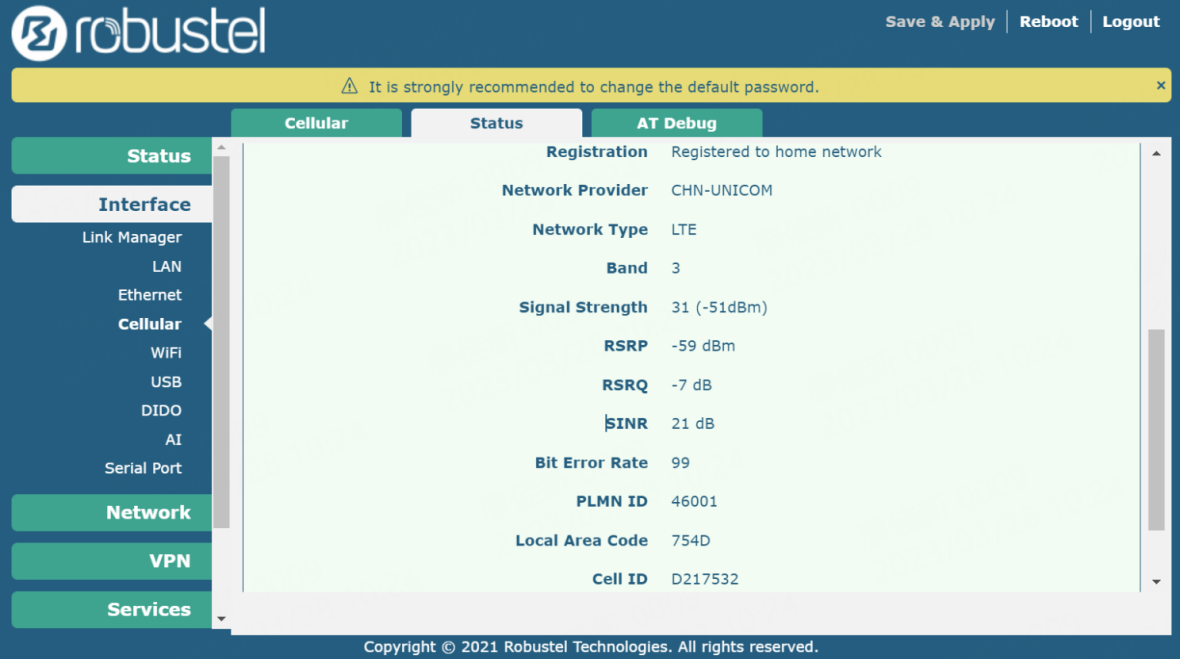
Measuring LTE Cat M1 Network Signal Quality
Below all are RSRP dBm
- Rx <= -105 dBm, override strength level: 6. Poor coverage. The business is basically unable to call.
- -105 dBm < Rx <= -95 dBm, level 5. Poor coverage. Outdoor voice services can make calls, but the call success rate is low and the call drop rate is high. Indoor services basically cannot initiate services.
- -95 dBm < Rx <= -85 dBm, level 4. The coverage is fair, various services can be initiated outdoors, and low-rate data services can be obtained. However, the success rate of indoor calls is low and the call drop rate is high.
- -85 dBm < Rx <= -75 dBm, level 3. The coverage is good, various services can be initiated outdoors, and medium-rate data services can be obtained. Various services can be initiated indoors to obtain low-rate data services.
- -75 dBm Rx <= -65 dBm, level 2. With good coverage, various services can be initiated outdoors to obtain high-speed data services. Various services can be initiated indoors, and medium-rate data services can be obtained.
- Rx > -65 dBm, level 1. Coverage is very good.
Measuring NB-IoT Network Signal Quality
It‘s generally judged comprehensively by RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power) and SNR (Signal-to-Noise Ratio) values.
- When RSRP >-100 dBm and SNR > 3 dB, the service is relatively stable and the success rate is high.
- When -110 dBm<RSRP<-100 dBm and -3 dB <SNR<3 dB, the service stability is relatively poor, and the success rate may will affect.
- When RSRP<-115 dBm or SNR <-3 dB, the probability of service failure is relatively high, which affects the service success rate

